[Android] Paging3 Pager 내부에서 일어나는 일
이전 글에서 PagingDataAdapter의 submitData에 대해서 알아보았다 이전 글 : Paging3 PagingAdater가 UI를 업데이트하기까지
Paging3 version 3.0.1
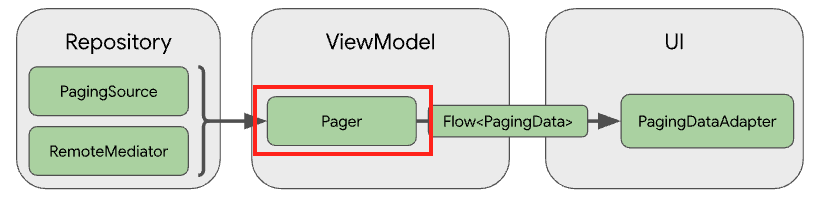
이번엔 Pager에 대해 알아보자.
Pager는 PagingSource 나 RemoteMediator와 PageConfig의 정보를 토대로 PagingData를 생성한 뒤 스트림화 해주는 클래스이다. 스트림화 시에는 Flow, LiveData, RxJava와 같은 Flowable 유형과 Observable유형 모두를 지원한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// Pager.kt
public class Pager<Key : Any, Value : Any>
// Experimental usage is propagated to public API via constructor argument.
@ExperimentalPagingApi constructor(
config: PagingConfig,
initialKey: Key? = null,
remoteMediator: RemoteMediator<Key, Value>?,
pagingSourceFactory: () -> PagingSource<Key, Value>
) {
// Experimental usage is internal, so opt-in is allowed here.
@JvmOverloads
@OptIn(ExperimentalPagingApi::class)
public constructor(
config: PagingConfig,
initialKey: Key? = null,
pagingSourceFactory: () -> PagingSource<Key, Value>
) : this(config, initialKey, null, pagingSourceFactory)
}
Pager.kt 의 모습이다
기본생성자와 부생성자가 있는데 파라미터로 remoteMediator를 받느냐 아니냐의 차이가 존재한다
먼저 PagingConfig에 대해서 알아보자
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
PagingConfig
// PagingConfig.kt
public class PagingConfig @JvmOverloads public constructor(
@JvmField
public val pageSize: Int,
@JvmField
@IntRange(from = 0)
public val prefetchDistance: Int = pageSize,
@JvmField
public val enablePlaceholders: Boolean = true,
@JvmField
@IntRange(from = 1)
public val initialLoadSize: Int = pageSize * DEFAULT_INITIAL_PAGE_MULTIPLIER,
@JvmField
@IntRange(from = 2)
public val maxSize: Int = MAX_SIZE_UNBOUNDED,
@JvmField
public val jumpThreshold: Int = COUNT_UNDEFINED
) {
init {
if (!enablePlaceholders && prefetchDistance == 0) {
throw IllegalArgumentException(
"Placeholders and prefetch are the only ways" +
" to trigger loading of more data in PagingData, so either placeholders" +
" must be enabled, or prefetch distance must be > 0."
)
}
if (maxSize != MAX_SIZE_UNBOUNDED && maxSize < pageSize + prefetchDistance * 2) {
throw IllegalArgumentException(
"Maximum size must be at least pageSize + 2*prefetchDist" +
", pageSize=$pageSize, prefetchDist=$prefetchDistance" +
", maxSize=$maxSize"
)
}
require(jumpThreshold == COUNT_UNDEFINED || jumpThreshold > 0) {
"jumpThreshold must be positive to enable jumps or COUNT_UNDEFINED to disable jumping."
}
}
public companion object {
@Suppress("MinMaxConstant")
public const val MAX_SIZE_UNBOUNDED: Int = Int.MAX_VALUE
internal const val DEFAULT_INITIAL_PAGE_MULTIPLIER = 3
}
}
PagingConfig는 페이징 소스에서 콘텐츠를 로드할 때 Pager 내에서 로드 동작을 구성하는 데 사용되는 객체이다. 생성자로 넘겨줄 파라미터 값들을 하나하나 살펴보자.
- pageSize
- PagingSource에서 한 번에 로드될 항목의 수를 의미한다.
- pageSize는 데이터가 로드되고, 사용되는 방식에 따라서 다르게 설정해야 한다.
- 화면의 대부분을 차지하는 큰 소셜 미디어 스타일의 카드에 대한 데이터를 로드하고, 데이터베이스가 병목이 일어나지 않는다면 10-20이 적당하다.
- 스크롤하는 동안 데이터를 빠르게 표시할 수 있는 그리드 형식의 수십개의 아이템을 표시하는 경우에는 100에 가까운 값이 적당할 수 있다.
- prefetchDistance
- PagedList 의 최상단/최하단에 도달하기 얼마 전에 추가 로딩을 수행할지에 대한 설정값이다.
- 기본값으로 pageSize가 설정되어있다
- enablePlaceHolders
- 가져올 페이지가 없는 경우 placeHolder를 표시할것인지에 대한 설정값이다.
- PagingSource에서 아직 로드되지 않은 아이템의 갯수(null 갯수)에 따라서 placeHolder 표시
- initialLoadSize
- PagingSouce가 처음으로 로드할 페이지의 크기를 설정한다.
- 기본값으로 넘겨받은 pageSize와
DEFAULT_INITIAL_PAGE_MULTIPLIER를 곱한 값을 사용한다.
- maxSize
- 페이지를 삭제하기 전에 페이징 데이터로 로드할 수 있는 최대 항목 수를 설정하는 값
- maxSizes는 최소 prefetchDistance * 2 + pageSize 로 설정되어야 한다.
- maxSize를 사용해 페이지를 삭제해 메모리에 저장된 항목 수를 제한할 수 있다.
- 기본값은
MAX_SIZE_UNBOUNDED로 되어있으며, 이 경우 페이지가 삭제되지 않는다.
- jumpthreshold
- 페이징이 페이지 로드를 점진적으로 포기하고 대신 무효화를 통해 새로 고침을 트리거하여 사용자의 위치로 이동하기 전에 로드된 항목의 범위를 벗어나 스크롤된 항목 수에 대한 임계값을 설정한다.
- 해당 내용에 대해서는 따로 포스팅할 예정이다..
- 마지막으로 init 블록인데 여기서 파라미터들에 대한 설정값들을 검증해주고 있다.
1
initialKey
- Pager에 전달될 key에 대한 type이 지정된다.
1
remoteMediator
- 로컬 db캐싱에 사용될 RemoteMediator 클래스를 구현한 클래스가 지정된다.
1
pagingSourceFactory
- PagingSource를 구현한 클래스가 지정된다.
Stream 형태의 pagingData로 변환
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
fun getDataStream(query: String): Flow<PagingData<Repo>> {
return Pager(
config = PagingConfig(
pageSize = PAGER_SIZE,
enablePlaceholders = false
),
pagingSourceFactory = { SomeRepo() }
).flow
}
companion object {
const val PAGER_SIZE = 30
}
Flow 형태의 Stream으로 변환하기 위해서 .flow 를 사용한다.
내부를 살펴보자
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// Pager.kt
public val flow: Flow<PagingData<Value>> = PageFetcher(
pagingSourceFactory = if (
pagingSourceFactory is SuspendingPagingSourceFactory<Key, Value>
) {
pagingSourceFactory::create
} else {
// cannot pass it as is since it is not a suspend function. Hence, we wrap it in {}
// which means we are calling the original factory inside a suspend function
{
pagingSourceFactory()
}
},
initialKey = initialKey,
config = config,
remoteMediator = remoteMediator
).flow
Pager의 flow는 내부적으로 PagerFetcher의 flow를 사용한다.
Pager의 flow는 넘겨받은 pagingSourceFactory가 SuspendingPagingSourceFactory인지 확인한 후 pagingSource를 그대로 사용하거나 {}로 wrap한다.
그렇다면 PagerFetcher의 flow는 어떻게 구현되어 있을까?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
// PageFetcher.kt
// The object built by paging builder can maintain the scope so that on rotation we don't stop
// the paging.
val flow: Flow<PagingData<Value>> = simpleChannelFlow {
val remoteMediatorAccessor = remoteMediator?.let {
RemoteMediatorAccessor(this, it)
}
refreshEvents // #1
.flow
.onStart {
@OptIn(ExperimentalPagingApi::class)
emit(remoteMediatorAccessor?.initialize() == LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH)
}
.simpleScan(null) { previousGeneration: GenerationInfo<Key, Value>?, // #2
triggerRemoteRefresh: Boolean ->
var pagingSource = generateNewPagingSource( // #3
previousPagingSource = previousGeneration?.snapshot?.pagingSource
)
while (pagingSource.invalid) {
pagingSource = generateNewPagingSource(previousPagingSource = pagingSource)
}
var previousPagingState = previousGeneration?.snapshot?.currentPagingState()
if (previousPagingState?.pages.isNullOrEmpty() && // #4
previousGeneration?.state?.pages?.isNotEmpty() == true
) {
previousPagingState = previousGeneration.state
}
if (previousPagingState?.anchorPosition == null && // #5
previousGeneration?.state?.anchorPosition != null
) {
previousPagingState = previousGeneration.state
}
val initialKey: Key? = previousPagingState?.let { pagingSource.getRefreshKey(it) }
?: initialKey
previousGeneration?.snapshot?.close()
GenerationInfo(
snapshot = PageFetcherSnapshot(
initialKey = initialKey,
pagingSource = pagingSource,
config = config,
retryFlow = retryEvents.flow,
triggerRemoteRefresh = triggerRemoteRefresh,
remoteMediatorConnection = remoteMediatorAccessor,
invalidate = this@PageFetcher::refresh,
previousPagingState = previousPagingState,
),
state = previousPagingState,
)
}
.filterNotNull()
.simpleMapLatest { generation ->
val downstreamFlow = generation.snapshot
.injectRemoteEvents(remoteMediatorAccessor)
PagingData(
flow = downstreamFlow,
receiver = PagerUiReceiver(generation.snapshot, retryEvents)
)
}
.collect { send(it) }
}
주석에 따르면 PagerFetcher에 내장된 flow객체로 페이징을 작성하면 회전 시 페이징을 중지 하지 않도록 스코프를 유지한다고 한다.
#1
1
private val refreshEvents = ConflatedEventBus<Boolean>()
- refreshEvents는 StateFlow를 기반으로 하는 Conflated Broadcast Channel과 같은 역할을 하는 간단한 버스로서 PageFetcherSnapshot의 새 인스턴스를 트리거하는 새로 고침 신호의 채널이다.
- REFRESH 로드가 트리거 되어야 한다면 해당 채널에 send(true)를, 아니면 send(false)를 해주면 된다.
- 해당 채널은 버퍼 크기가 1이며 항상 가장 최근에 수신된 값을 브로드캐스트한다.
#2
1
.simpleScan(null) { ... }
- simpleScan은 paging 내부에서 experimental API를 사용하지 않도록 구현한 extension 함수이다
- scan은 상태변수를 선언하지 않고 해당 값을 유지시키며 값이 들어올 때마다 그 상태 누적값을 계속 변화시킨다
#3
1
2
3
4
5
6
var pagingSource = generateNewPagingSource(
previousPagingSource = previousGeneration?.snapshot?.pagingSource
)
while (pagingSource.invalid) {
pagingSource = generateNewPagingSource(previousPagingSource = pagingSource)
}
- paingSource를 갱신시켜주는 로직
- pagingSource가 invalid하면 generateNewPagingSource에서 Pager를 만들때 넘겨받은 pagingSource로 갱신시켜준다.
#4
1
2
3
4
5
if (previousPagingState?.pages.isNullOrEmpty() &&
previousGeneration?.state?.pages?.isNotEmpty() == true
) {
previousPagingState = previousGeneration.state
}
- 캐시된 PagingState에 페이지가 로드되었지만 이전 세대에는 로드되지 않은 경우 캐시된 PagingState를 사용하여 무효화가 너무 빨리 발생하는 경우를 처리하여 getRefreshKey 및 원격 새로 고침에 최소한 작업할 데이터가 있도록 한다
#5
1
2
3
4
5
if (previousPagingState?.anchorPosition == null &&
previousGeneration?.state?.anchorPosition != null
) {
previousPagingState = previousGeneration.state
}
- anchorPosition이 설정되기 전에 previousGeneration이 무효화된 경우 페이지를 성공적으로 로드하고 anchorPosition이 있는 마지막 PagingState를 다시 사용한다. 이렇게 하면 previousGeneration이 비활성화되기 전에 로드할 시간이 없었던 경우 빠른 비활성화로 인해 anchorPosition이 삭제되는 것을 방지할 수 있다.
snapshot과 state로 구성된 GenerationInfo를 만들고 이를 mapping해 PagingData를 구성한다